New Chapter 7 means test numbers take effect November 1, 2017. The means test numbers purport to state the median income per family size based on jurisdiction. To file a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you must qualify under the Chapter 7 bankruptcy means test. In most cases, your income must be less than or equal to the median income for your family size in your state to qualify for Chapter 7.
Here are the new Chapter 7 means test numbers for the Washington, D.C. region:
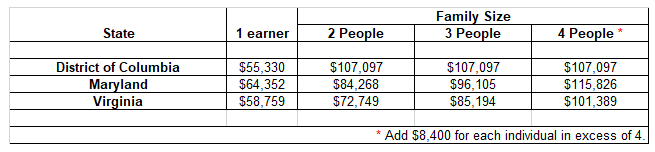
Note that the median incomes for 2-person, 3-person, and 4-person households in D.C. are exactly the same. I have previously noted that the D.C. means test numbers are patently unjust. The U.S. Trustee’s Office states that the Chapter 7 means test numbers are based on U.S. Bureau of Census data.
New Chapter 7 means test numbers: Analysis
The previous means test numbers, applicable to cases filed from May 1, 2017 to October 31, 2017, are no longer operative. All three jurisdictions in the D.C. area have apparently experienced an increase in income.
The means test numbers for Washington, D.C. saw an aggregate income increase of $13,144, or 3.6 percent. Maryland increased $10,139 (2.9 percent), while Virginia aggregate income increase $9,638 (3.1 percent).
The biggest changes in the new Chapter 7 means test numbers were for 2-person and 3-person households in the District, which saw an $8,051 increase. The smallest change in the new numbers was for a single-person household in Maryland, which increased just $951.
How do the new Chapter 7 means test numbers affect you?
For some households, the ability to pass the means test may change from month to month. For other households, the means test represents an absolute bar to filing under Chapter 7. Talk to an experienced bankruptcy attorney to determine whether you qualify for a Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
